Receive Comprehensive Health Care at L.T Way to Healthcare, Bhubaneswar.
waytohealthcarebbsr@gmail.com
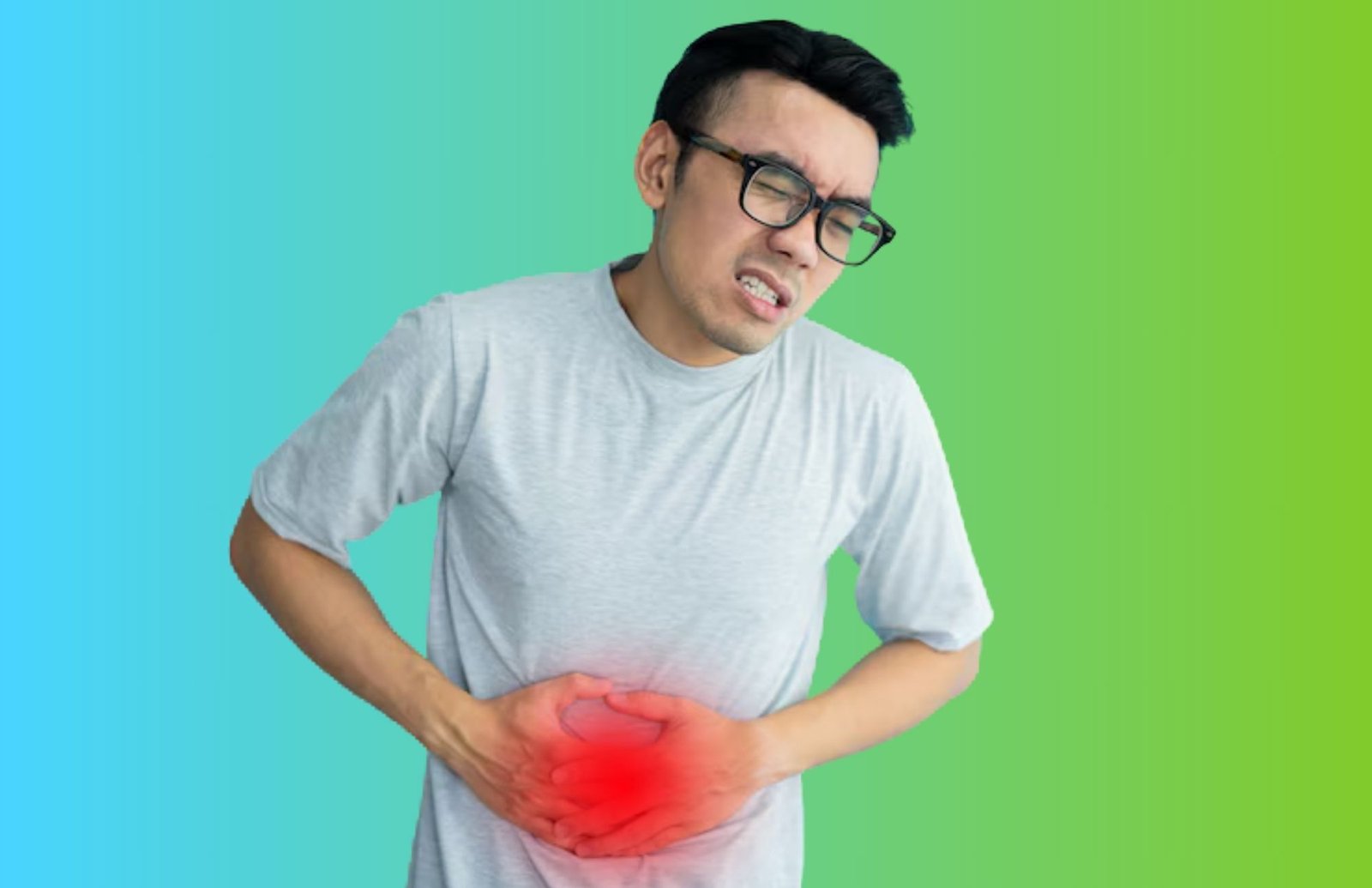
Less Common: Chronic appendicitis occurs less frequently than acute appendicitis.
Symptoms: Mild to moderate pain, intermittent abdominal discomfort, nausea.
Severity: Symptoms are often vague and less specific.
Treatment: Appendectomy is typically required.
Urgency: Less urgent than acute appendicitis but needs timely medical attention.
Appendicitis is an infection or inflammation of the appendix, a small tube attached to the large intestine. Its exact cause is unclear, but factors like blockage, infection, or digestive tract issues can contribute to its development, leading to pain and complications.
Lymphoid hyperplasia is the abnormal increase of lymphoid cells or tissues, part of the immune system. It occurs due to infection, inflammation, or immune responses, causing enlargement of lymph nodes, spleen, or mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues like tonsils and Peyer’s patches.
Parasites are organisms that live on or inside another organism (the host) and benefit at the host’s expense. They can cause a variety of diseases and health problems, depending on the type of parasite and the affected body system.
Tumors are abnormal growths of cells or tissues that can occur in any part of the body. They arise when cells grow uncontrollably due to mutations or other changes in their genetic material. Tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
A blockage refers to an obstruction or clog in a passage or system, preventing the normal flow of substances, such as fluids, gases, or solids. Blockages can occur in various parts of the body, such as blood vessels, digestive tract, or airways, and can have different causes, depending on the location and nature of the blockage.

